- Understanding the Role of Geomembrane Liners in Waste Management
- Innovations in Geomembrane Liners for Water Management
- Geomembrane Liners: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Future of Geomembrane Liners in Civil Engineering
- Geomembrane Liners: Enhancing Landfill Stability
Manager:
WhatsApp:+86 177 0135 2670
Tel:+86 177 0135 2670
Email:marketing@okorder.com
Address:3rd Floor, No.2 Building, No.1 Sanlihe Road
Is HDPE stronger than polycarbonate?
Composite geomembranes play a crucial role in various engineering applications, from environmental protection to hydraulic engineering. Among the materials commonly used in manufacturing composite geomembranes, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) geomembranes stand out for their exceptional strength and durability. However, when comparing HDPE to other materials like polycarbonate, the question arises: Is HDPE truly stronger? Let's delve into the characteristics of both materials to find the answer.

Understanding Composite Geomembranes
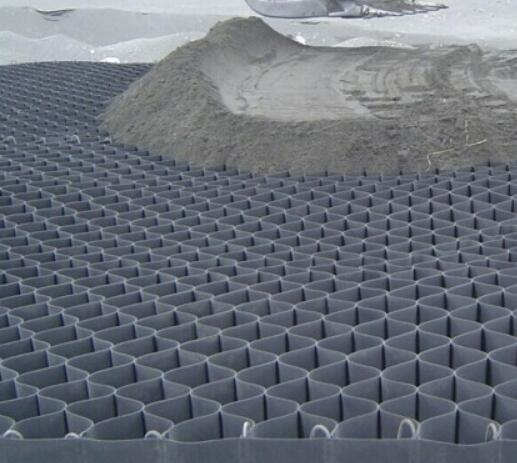
Composite geomembranes consist of multiple layers of different materials bonded together to create a robust barrier against fluid migration and environmental contaminants. These materials are engineered to withstand harsh conditions and provide long-term performance in applications such as landfill liners, pond liners, and water containment systems.
The Strength of hdpe Geomembranes
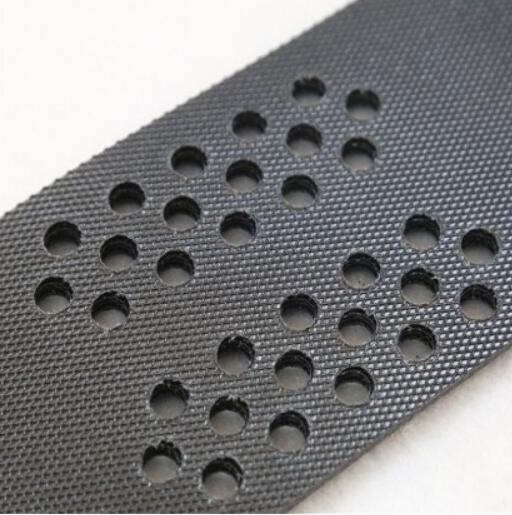
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) geomembranes are renowned for their exceptional strength and durability. HDPE is a type of thermoplastic polymer known for its high tensile strength, puncture resistance, and chemical inertness. These properties make HDPE geomembranes highly suitable for applications where strength and durability are paramount.
HDPE geomembranes exhibit impressive mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and tear resistance. This enables them to withstand significant loads and environmental stresses without compromising their integrity. Additionally, HDPE geomembranes have excellent resistance to chemical and biological degradation, ensuring long-term performance in diverse environmental conditions.
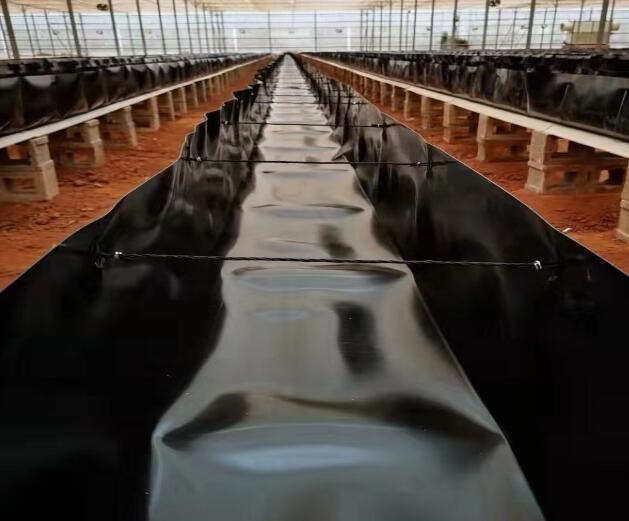
In applications such as landfill liners and mining containment, where exposure to harsh chemicals and abrasive materials is common, HDPE geomembranes provide reliable protection against fluid migration and environmental contamination. Their robustness and resistance to punctures make them an ideal choice for safeguarding sensitive ecosystems and groundwater resources.
Comparing HDPE to Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is another material that finds use in various engineering applications due to its desirable properties, including high impact resistance and transparency. However, when it comes to strength and durability, HDPE outperforms polycarbonate in several key aspects.
While polycarbonate offers excellent impact resistance and optical clarity, it falls short in terms of tensile strength and puncture resistance compared to HDPE. HDPE geomembranes are specifically engineered to withstand high loads and environmental stresses, making them more suitable for applications requiring superior strength and durability.
In applications where the primary concern is mechanical strength and resistance to punctures, such as landfill liners and containment barriers, HDPE geomembranes provide a more reliable solution than polycarbonate. The robustness of HDPE ensures long-term performance and protection against fluid migration, while polycarbonate may be prone to damage under similar conditions.
The Role of Composite Geomembranes
Composite geomembranes leverage the strengths of different materials to create a multifaceted barrier against fluid migration and environmental contaminants. By combining layers of HDPE, along with other materials such as Geotextiles and geonet, composite geomembranes offer enhanced performance and versatility in various applications.
The inclusion of HDPE geomembranes in composite systems enhances their overall strength and durability, while other layers provide additional functionalities such as filtration and drainage. This synergy results in composite geomembranes that can withstand a wide range of environmental conditions and mechanical stresses, ensuring reliable performance over the long term.
In conclusion, while both HDPE and polycarbonate offer unique advantages in their respective applications, HDPE stands out as the stronger and more durable choice for composite geomembranes. Its exceptional mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and puncture resistance, make it an ideal material for applications requiring robust barrier systems. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each material, engineers and designers can make informed decisions when selecting geomembranes for their projects, ensuring optimal performance and environmental protection."
-
2024-06-13Geomembrane is not plastic cloth






